Mossy Fiber (hippocampus) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In the
In the
hippocampus
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, a ...
, the mossy fiber pathway consists of unmyelinated
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be l ...
axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action po ...
s projecting from granule cell
A granule is a large particle or grain. It can refer to:
* Granule (cell biology), any of several submicroscopic structures, some with explicable origins, others noted only as cell type-specific features of unknown function
** Azurophilic granul ...
s in the dentate gyrus
The dentate gyrus (DG) is part of the hippocampal formation in the temporal lobe of the brain, which also includes the hippocampus and the subiculum. The dentate gyrus is part of the hippocampal trisynaptic circuit and is thought to contribute ...
that terminate on modulatory hilar mossy cells and in Cornu Ammonis area 3 (CA3), a region involved in encoding short-term memory
Short-term memory (or "primary" or "active memory") is the capacity for holding a small amount of information in an active, readily available state for a short interval. For example, short-term memory holds a phone number that has just been recit ...
. These axons were first described as mossy fibers by Santiago Ramón y Cajal
Santiago Ramón y Cajal (; 1 May 1852 – 17 October 1934) was a Spanish neuroscientist, pathologist, and histologist specializing in neuroanatomy and the central nervous system. He and Camillo Golgi received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Med ...
as they displayed varicosities along their lengths that gave them a mossy appearance. The axons that make up the pathway emerge from the basal portions of the granule cells and pass through the hilus (or polymorphic cell layer) of the dentate gyrus
The dentate gyrus (DG) is part of the hippocampal formation in the temporal lobe of the brain, which also includes the hippocampus and the subiculum. The dentate gyrus is part of the hippocampal trisynaptic circuit and is thought to contribute ...
before entering the stratum lucidum
The stratum lucidum (Latin, 'clear layer') is a thin, clear layer of dead skin cells in the epidermis named for its translucent appearance under a microscope. It is readily visible by light microscopy only in areas of thick skin, which are found ...
of CA3. Granule cell synapses tend to be glutamatergic
Glutamatergic means "related to glutamate". A glutamatergic agent (or drug) is a chemical that directly modulates the excitatory amino acid (glutamate/ aspartate) system in the body or brain. Examples include excitatory amino acid receptor agonist ...
(i.e. excitatory), though immunohistological data has indicated that some synapses contain neuropeptidergic elements including opiate
An opiate, in classical pharmacology, is a substance derived from opium. In more modern usage, the term ''opioid'' is used to designate all substances, both natural and synthetic, that bind to opioid receptors in the brain (including antagonis ...
peptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A ...
s such as dynorphin
Dynorphins (Dyn) are a class of opioid peptides that arise from the precursor protein prodynorphin. When prodynorphin is cleaved during processing by proprotein convertase 2 (PC2), multiple active peptides are released: dynorphin A, dynorphin B, a ...
and enkephalin
An enkephalin is a pentapeptide involved in regulating nociception in the body. The enkephalins are termed endogenous ligands, as they are internally derived and bind to the body's opioid receptors. Discovered in 1975, two forms of enkephalin ...
. There is also evidence for co-localization of both GABAergic
In molecular biology and physiology, something is GABAergic or GABAnergic if it pertains to or affects the neurotransmitter GABA. For example, a synapse is GABAergic if it uses GABA as its neurotransmitter, and a GABAergic neuron produces GABA. A ...
(i.e. inhibitory) and glutamatergic
Glutamatergic means "related to glutamate". A glutamatergic agent (or drug) is a chemical that directly modulates the excitatory amino acid (glutamate/ aspartate) system in the body or brain. Examples include excitatory amino acid receptor agonist ...
neurotransmitters within mossy fiber terminals. GABAergic and glutamatergic co-localization in mossy fiber boutons has been observed primarily in the developing hippocampus, but in adulthood, evidence suggests that mossy fiber synapses may alternate which neurotransmitter is released through activity-dependent regulation.
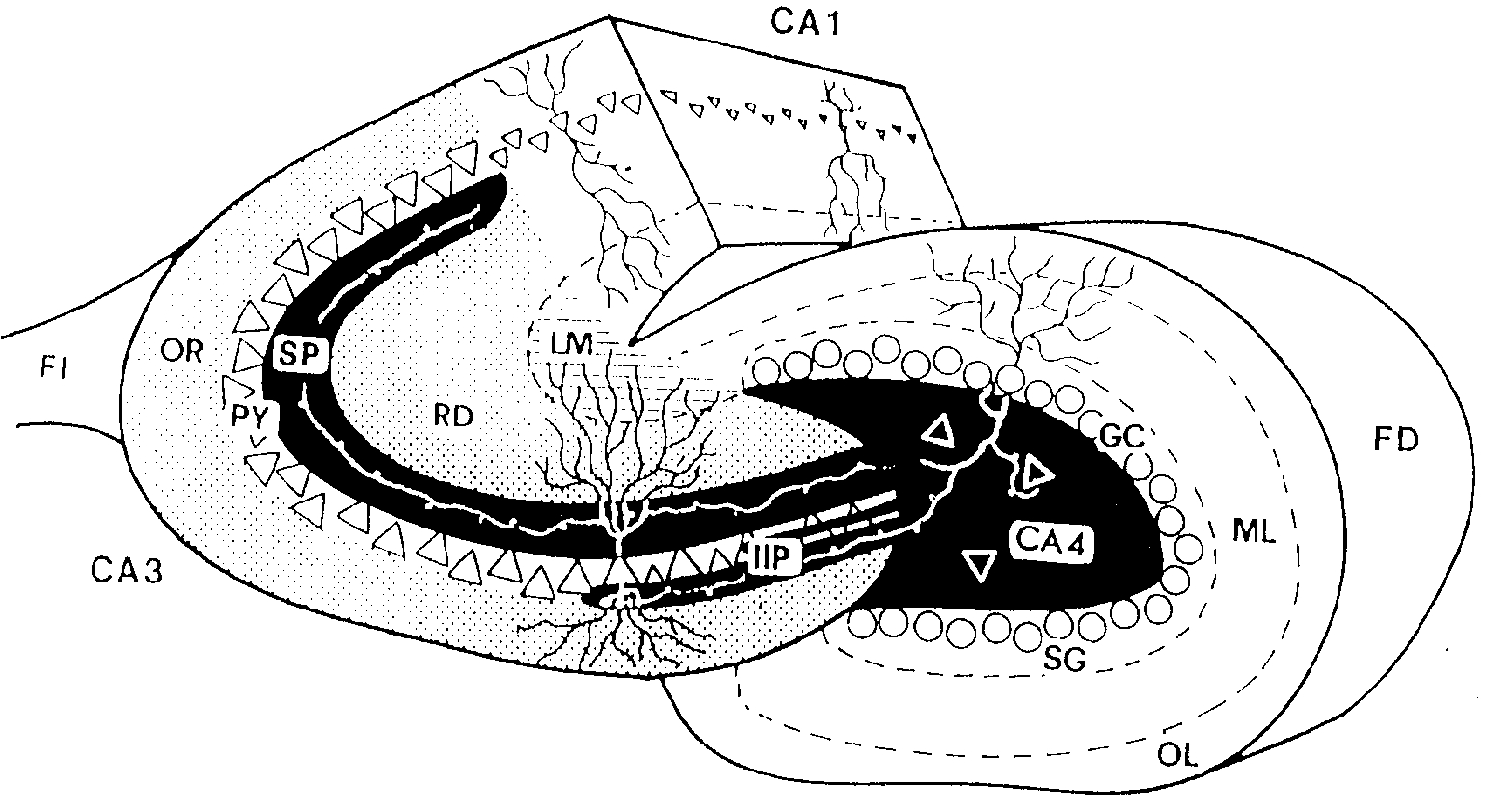
Anatomy
Mossy fibers in the hippocampus project from thedentate gyrus
The dentate gyrus (DG) is part of the hippocampal formation in the temporal lobe of the brain, which also includes the hippocampus and the subiculum. The dentate gyrus is part of the hippocampal trisynaptic circuit and is thought to contribute ...
to CA3. The pathway consists of varicose granule cell axons that terminate on the dendrite
Dendrites (from Greek δένδρον ''déndron'', "tree"), also dendrons, are branched protoplasmic extensions of a nerve cell that propagate the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body, or soma, of the n ...
s of hilar mossy cells and pyramidal cells in CA3. They form three morphologically different synaptic terminals, which include large mossy terminals, filopodial extensions within the mossy terminals, and small ''en passant'' synaptic varicosities. Each of these synapse types is functionally distinct.
Synaptic terminals
Mossy fibers form multiple synapses with the elaborate dendritic spines of CA3pyramidal cell
Pyramidal cells, or pyramidal neurons, are a type of multipolar neuron found in areas of the brain including the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, and the amygdala. Pyramidal neurons are the primary excitation units of the mammalian prefrontal cor ...
s in the stratum lucidum of the hippocampus. These complex spines are known as "thorny excrescences." Thorny excrescences also cover the proximal dendrites of mossy cells in the hilus. Hilar thorny excrescences are more dense and complex than those in CA3. It has been shown that the axons of granule cells from the dentate gyrus synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell.
Synapses are essential to the transmission of nervous impulses from ...
with hilar mossy cells and GABAergic interneuron
Interneurons (also called internuncial neurons, relay neurons, association neurons, connector neurons, intermediate neurons or local circuit neurons) are neurons that connect two brain regions, i.e. not direct motor neurons or sensory neurons. I ...
s including basket cell
Basket cells are inhibitory GABAergic interneurons of the brain, found throughout different regions of the cortex and cerebellum.
Anatomy and physiology
Basket cells are multipolar GABAergic interneurons that function to make inhibitory synapses ...
s before reaching pyramidal cell
Pyramidal cells, or pyramidal neurons, are a type of multipolar neuron found in areas of the brain including the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, and the amygdala. Pyramidal neurons are the primary excitation units of the mammalian prefrontal cor ...
s in the CA3 region, providing input from the entorhinal cortex
The entorhinal cortex (EC) is an area of the brain's allocortex, located in the medial temporal lobe, whose functions include being a widespread network hub for memory, navigation, and the perception of time.Integrating time from experience in the ...
through the perforant path
In the brain, the perforant path or perforant pathway provides a connectional route from the entorhinal cortex to all fields of the hippocampal formation, including the dentate gyrus, all CA fields (including CA1), and the subiculum.
Though it a ...
way. Hilar mossy cell activation is thought to be necessary for the proper function of these inhibitory basket cells on CA3 pyramidal cells, although evidence has shown that sodium channel receptors can regulate basket cell function as well.
The three synaptic terminals types – mossy terminals, filopodial extensions, and en passant synaptic varicosities – differ in synaptic output. Large mossy terminals synapse with 11–15 different CA3 pyramidal cells and 7–12 mossy cells. ''En passant'' boutons with 25–35 synaptic connections and filopodial extensions with 12–17 make up a significant portion of total granule cell synaptic terminals and are mainly responsible for the excitation of GABAergic interneurons. The type of synaptic terminal expressed therefore dictates the downstream targeting of granule cells. The high convergence onto pyramidal cells and divergent projections onto interneurons suggests a primarily modulatory role for the mossy fiber pathway in the hippocampus.
The synapses of the mossy fibers contain zinc, which can be stained with a Timm staining.
Projections
The dentate gyrus receives excitatory projections from neurons in layer II of the entorhinal cortex as well as input from surroundingneuroglia
Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system that do not produce electrical impulses. They maintain homeostasis, form mye ...
. The unmyelinated granule cell axons of the mossy fiber pathway express both GABA receptor
The GABA receptors are a class of receptors that respond to the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the chief inhibitory compound in the mature vertebrate central nervous system. There are two classes of GABA receptors: GABAA and ...
s and glutamate receptors
Glutamate receptors are synaptic and non synaptic receptors located primarily on the membranes of neuronal and glial cells. Glutamate (the conjugate base of glutamic acid) is abundant in the human body, but particularly in the nervous system an ...
along their membranes
A membrane is a selective barrier; it allows some things to pass through but stops others. Such things may be molecules, ions, or other small particles. Membranes can be generally classified into synthetic membranes and biological membranes. Bi ...
that allow them to be modulated by both excitatory and inhibitory input from nearby glial cells. Axons from the entorhinal cortex synapse primarily on the dendritic spines of outer layer dentate granule cells. The entorhinal cortex passes sensory information from neocortical structures to the hippocampal formation
The hippocampal formation is a compound structure in the Temporal lobe#Medial temporal lobe, medial temporal lobe of the brain. It forms a c-shaped bulge on the floor of the temporal horn of the Lateral ventricles, lateral ventricle. There is no ...
. The pathway allows sensory information to reach the hippocampus for encoding.
The mossy fiber pathway itself projects to CA3. Repetitive stimulation of its neurons leads to progressive use-dependent synaptic depression. These short-term changes in plasticity
Plasticity may refer to:
Science
* Plasticity (physics), in engineering and physics, the propensity of a solid material to undergo permanent deformation under load
* Neuroplasticity, in neuroscience, how entire brain structures, and the brain it ...
have been shown to be mediated by sodium channels that receive input from neuroglia. The entorhinal cortex also projects directly to CA3, suggesting that the mossy fiber pathway may be functionally similar to the perforant pathway although microcircuits within the dentate gyrus give the mossy fiber pathway a more modulatory role. Projections to the dentate hilus are excitatory by nature and oppose the inhibitory effects of interneurons on hilar mossy cells. The result is an excitatory feedforward loop on mossy cells as a result of activation by the entorhinal cortex.
Role in learning and memory
In the mouse, a single mossy fiber projection may make as many as 37 contacts with a singlepyramidal cell
Pyramidal cells, or pyramidal neurons, are a type of multipolar neuron found in areas of the brain including the cerebral cortex, the hippocampus, and the amygdala. Pyramidal neurons are the primary excitation units of the mammalian prefrontal cor ...
, but innervates only about a dozen different pyramidal cells. In contrast, a single CA3 pyramidal cell receives input from about 50 different granule cells. It has been shown in rodents that the size of the mossy fiber projections can show large interindividual variations, which are to a large part heritable. In addition, these variations show strong correlations with different types of behavior, mainly, but not exclusively, spatial learning
In cognitive psychology and neuroscience, spatial memory is a form of memory responsible for the recording and recovery of information needed to plan a course to a location and to recall the location of an object or the occurrence of an event. Sp ...
.
See also
*Mossy fiber (cerebellum)
Mossy fibers are one of the major inputs to cerebellum. There are many sources of this pathway, the largest of which is the cerebral cortex, which sends input to the cerebellum via the pontocerebellar pathway. Other contributors include the ves ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mossy Fiber (Hippocampus) Hippocampus (brain)